Imagine a world where your electricity bill is a fraction of what it is today, or even nonexistent, because you’ve mastered how to generate electricity at home for free. This isn’t a pipe dream. By harnessing the natural resources abundant around us—sun, wind, water, or even your own organic waste—you can gain energy independence, significantly lower your carbon footprint, and save a substantial amount on utility costs. It’s about taking control of your power, transforming your home into a self-sufficient hub.
This guide will walk you through the most viable methods for residential power generation, from the widely adopted to the experimentally innovative, helping you understand how to generate electricity at home for free (or at least, for very low ongoing costs after the initial setup).
At a Glance: Your Path to Home Power
- Solar Power: Best for homes with ample sunlight. Expect significant upfront costs, but long-term savings and incentives.
- Wind Turbines: Ideal for properties with consistent, strong winds and minimal obstructions. Requires careful site assessment and adherence to local regulations.
- Biomass/Biogas: Perfect if your property generates a lot of organic waste. Converts waste into usable energy.
- Micro-Hydro: An excellent, consistent power source if you have a flowing stream or river. Requires professional assessment and permits.
- Backup Generators: Not for “free” generation, but crucial for emergency power resilience.
- DIY & Emerging Tech: Explore experimental magnetic generators (with caution!) or keep an eye on geothermal, hydrogen, or piezoelectric innovations.
- Key Takeaway: While the energy source is free, all systems require an initial investment. “Free” refers to the ongoing operational costs, free from utility bills.
Unlocking Your Home’s Power Potential: Where to Start
Before diving into specific technologies, assess your immediate environment. Do you get abundant sunshine? Is your property often breezy? Do you have a flowing stream or a consistent supply of organic waste? Your unique landscape dictates the most effective and cost-efficient method to generate your own power. Choosing wisely means not just saving money, but also ensuring a reliable, long-term power supply.
Solar Power: Harnessing the Sun’s Bounty
Solar panels are perhaps the most recognizable way to make electricity at home. They’re quiet, clean, and increasingly efficient, turning daylight into usable power for your home.
What You Need & How It Works
For solar to be effective, your home should receive at least four hours of peak sunlight per day. This means minimal shading from trees or other buildings, especially during midday. The process itself is straightforward: solar cells convert sunlight directly into DC (direct current) power. An inverter then transforms this DC into AC (alternating current), which is what your home appliances use. Any excess power can be stored in batteries for nighttime use or, even better, sold back to your utility company through “net metering” programs, further cutting your bills. This is a powerful way to make free power at home.
Types of Solar Panels and Their Efficiency
When you’re looking to generate electricity at home with solar, understanding panel types helps in making an informed choice:
- Monocrystalline: These are the black-hued, premium panels. With an efficiency of around 20%, they convert more sunlight into electricity in a smaller footprint, making them ideal for limited roof space. They are, however, the most expensive upfront.
- Polycrystalline: Distinguished by their blue, speckled appearance, these panels are more affordable, typically offering 16% efficiency. They perform well but are slightly less heat-tolerant than monocrystalline options.
- Thin-Film: The cheapest and most flexible option, thin-film panels offer 7-13% efficiency. While they require more space to generate the same amount of power, their flexibility makes them suitable for unconventional surfaces.
Installation & Cost Considerations
You can certainly attempt a DIY solar installation, especially for smaller systems, but professional installation is often recommended to maximize efficiency and ensure safety. Companies will assess your roof’s slope and direction (south-facing roofs typically receive the most sun in the Northern Hemisphere) to optimize placement.
Expect an upfront cost in the range of $15,000 to $20,000 for an average residential system. While this seems significant, numerous financing options, payment plans, and government incentives—like federal tax credits and state/local rebates—can dramatically reduce your out-of-pocket expenses. These incentives can make it much more feasible to make free electricity over the long term.
Small Wind Systems: Harnessing the Breezes
If your property is consistently windy, a small wind turbine could be your ticket to energy independence. Wind power is a reliable way to generate electricity at home, especially in areas less suited for solar.
Ideal Conditions and Local Regulations
Wind turbines thrive in flat areas with few tall buildings or trees, where the average wind speed is 14 mph (23 km/h) or more. Before you even consider installing one, check local zoning restrictions. Many wind systems need to be significantly taller than surrounding structures (e.g., 30 feet higher than anything within 500 feet), and local ordinances often impose height limits, sometimes around 35 feet (11 m). These regulations are crucial to navigate to get free electricity for your home.
Sizing Your System
Determining the right size involves a simple calculation to match your energy needs with available wind. The formula AEO = (0.01328)D^2V^3 helps estimate your Annual Energy Output (AEO) in kilowatt-hours per year, where D is the rotor diameter and V is the average annual wind speed in miles per hour. A professional assessment can fine-tune this for optimal results.
Cost of Wind Power
Budget approximately $5,120 per kilowatt needed for a small wind system. This cost can vary based on turbine size, tower height, and installation complexity. While the upfront investment is substantial, the “fuel”—wind—is entirely free.
Biomass or Biogas Systems: Turning Waste into Watts
If you have a farm, a large garden, or regularly generate significant organic waste, a biomass or biogas system offers a unique and sustainable way to produce your own electricity.
What Counts as Fuel?
These systems thrive on organic waste like wood chips, timber offcuts, paper, old crops, sewage, or animal manure. Biogas, in particular, is highly efficient for converting animal waste on farms. You essentially turn what would otherwise be discarded into a valuable energy source.
The Magic of Methane
The process involves collecting and decomposing these organic materials in an anaerobic environment (without oxygen). This decomposition creates methane and carbon dioxide—biogas. This biogas can then be used directly for heating, cooling, or cooking, and, crucially, to generate electricity. Burning methane in a controlled biogas system is far preferable to releasing it into the atmosphere, where it acts as a potent greenhouse gas. For those looking to produce your own free electricity from unexpected sources, this is a compelling option.
Installation and Expense
Biomass and biogas systems are often partially underground, requiring professional installation to ensure proper waste collection and efficient off-gas burning. The initial investment, typically between $3,000 and $4,000 per kilowatt needed, is often the highest cost, with ongoing maintenance usually quite low. This can be an affordable home electricity guide for specific situations.
Micro-Hydro Systems: Power from Flowing Water
For homes with an existing stream or a fast-flowing river on the property, a micro-hydro system can provide exceptionally consistent and reliable electricity. It’s one of the best ways to power your home if you have the natural resource.
Assessing Your Stream’s Potential
A professional assessment is critical. They will measure the “head” (the vertical distance the water falls, which determines pressure) and the “flow” (the quantity of water passing through per second). Both are crucial for calculating potential energy output.
Permits and Environmental Considerations
Be prepared for paperwork. You’ll need to obtain permits from your local county and research water rights, as diverting or using stream water can be a complex legal area. Also, consider the environmental impact on native species; responsible system design minimizes disruption.
Enduring Benefits
Micro-hydro systems offer impressive benefits:
- Consistent Power: Unlike solar or wind, they aren’t dependent on daily weather fluctuations, providing a steady supply.
- Longevity: Well-maintained systems can last for decades.
- Low Maintenance: Once installed, they typically require minimal ongoing upkeep.
Cost Insights
Expect costs to range from $1,500 to $2,000 per kilowatt. Similar to other renewable systems, the upfront installation cost constitutes the largest expense, but the continuous, free energy from the stream makes it an attractive long-term investment. This can truly power your home for free once installed.
Generators: Your Emergency Power Lifeline
While not a primary method for how to generate electricity at home for free, diesel or biodiesel generators are indispensable for emergency backup. They provide peace of mind during power outages and are a practical addition to any off-grid or hybrid setup.
Portable vs. Permanent
You have options:
- Portable Generators: Cheaper, easy to move, and perfect for occasional use or smaller needs during outages.
- Permanent Generators: Offer a long-term, whole-home solution, often integrating directly with your electrical panel.
Pros & Cons
- Pros: Generators are simple machines, relatively easy to maintain, and provide immediate power when you need it most. Diesel models are notably more fuel-efficient than their gas-powered counterparts.
- Cons: They can be noisy, and fuel costs can accumulate, especially if used frequently. Remember, they are a backup, not a “free” energy solution.
Investment Range
Costs for generators typically fall between $3,000 and $10,000, with portable units being the most budget-friendly.
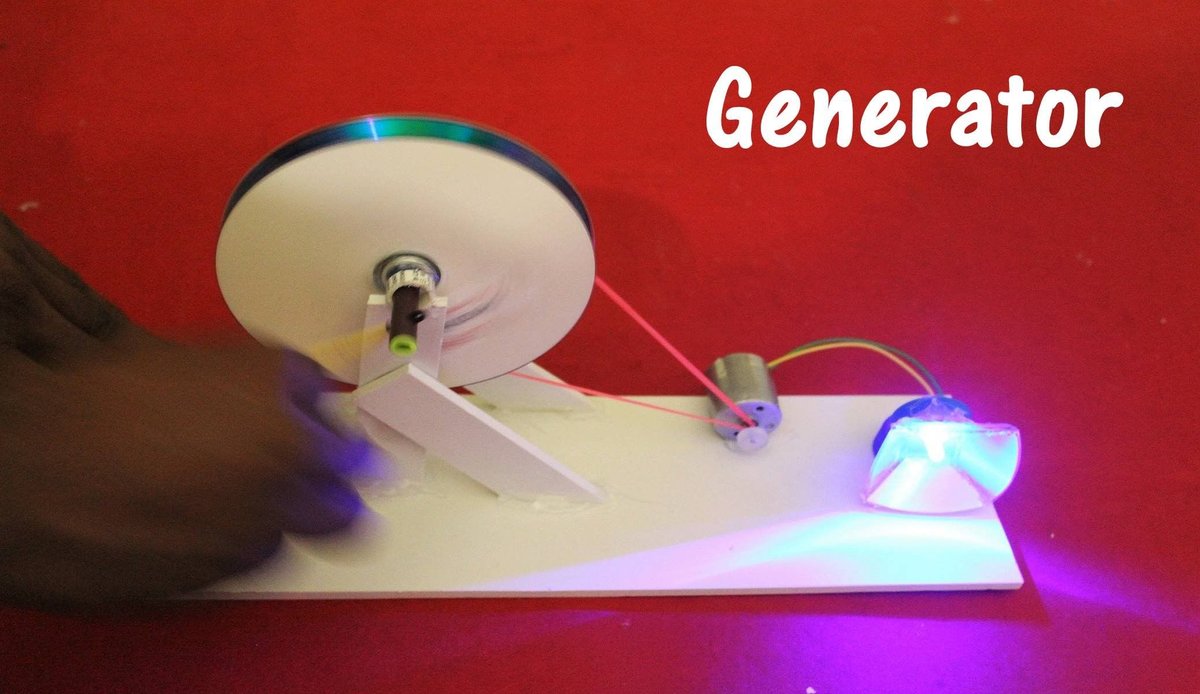
Stepping into the Unknown: DIY and Experimental Generators
For the truly curious and mechanically inclined, experimenting with small-scale, DIY generators offers a unique challenge. While “perpetual magnetic generators” have historically proven unreliable, the underlying principles of electromagnetism are real, offering a fascinating avenue to DIY free power solutions.
The Basic Concept: Magnetism and Electricity
These experimental setups aim to harness the fundamental relationship between magnetism and electricity. Moving a magnet near a coil of wire (or vice versa) induces an electric current—this is the principle behind many generators, large and small. It’s a hands-on way to explore unlock free energy secrets.
Essential Materials for Your Own Generator
To how to create electricity at a basic experimental generator, you’ll need:
- Strong Magnets: Neodymium magnets are highly recommended for their power.
- Thin Gauge Copper Wire: For wrapping coils.
- Sturdy Base: Wood or plastic to mount components.
- Platform/Spindle: To hold the coil or magnets in place for rotation.
- Switches, Capacitors: To control and store the generated energy.
- Basic Tools: Wire cutters, pliers, multimeter (essential for testing!).
Step-by-Step Construction (for an experimental magnetic coil generator)
- Construct Base and Platform: Start with a solid, level foundation. This provides stability for your components.
- Assemble Magnet and Coil: Secure a core (like a PVC pipe segment) and wrap approximately 100 turns of copper wire tightly around it to create a coil. Then, position your strong neodymium magnets very close to the coil without making contact. Experimentation with the precise distance and magnet arrangement is key for optimal effectiveness.
- Connect Wires: Identify the positive and negative ends of your coil. Use insulated copper wire to connect the coil to a switch, and then the switch to a capacitor in line. Double-check all connections to ensure they are secure and properly insulated to prevent shorts.
- Add Switch and Capacitor: Install a switch rated for the voltage and current you anticipate. A capacitor acts as a temporary battery, storing any generated energy. Connect these correctly to complete your circuit.
- Test and Troubleshoot: Activate your generator (e.g., manually spin the magnets past the coil, or if you’re ambitious, rig a small motor for continuous motion). Observe for any unusual sounds or vibrations. Use your multimeter to systematically check voltage and current output. Small adjustments to magnet/coil alignment can make a big difference. This hands-on process can help you start making free energy.
Safety First!
Working with electricity and strong magnets requires caution:
- Protection: Always wear protective eyewear and gloves.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Flammables: Keep flammable materials away from your setup.
- Fire Extinguisher: Have a fire extinguisher readily accessible.
- Realistic Expectations: Remember, while fascinating, claims of “perpetual magnetic generators” that defy the laws of thermodynamics have historically been debunked. This is an educational experiment, not a guaranteed home power solution.
Maintaining Your Experimental Setup
Periodically inspect all components for wear and tear, especially wiring insulation. Clean surfaces, ensure all connections remain tight, and document any changes in performance. This helps you understand the variables at play in your DIY free home electricity experiment.
The Horizon: Emerging and Innovative Methods
Beyond the established, several technologies are on the cusp of wider home application, promising even more diverse generate free power at home options.
- Geothermal Generators: Imagine tapping into the Earth’s internal heat! These systems utilize steam from hot water reservoirs beneath the surface, or even hot springs, to generate electricity. Primarily commercial, smaller residential units are being explored.
- Hydrogen Generators: Portable or small fixed hydrogen generators are becoming increasingly available. While hydrogen production itself requires energy, the ability to store and use it on-demand is a compelling prospect for free home electricity.
- Piezoelectric Generators: These fascinating devices harvest energy from vibrations or motion. Think about converting footsteps on a special floor or the sway of a building into electricity. While still largely experimental for whole-home power, small applications are emerging.
- Rainwater Generators: An experimental technology, these systems aim to capture the gravitational potential energy of falling rainwater. Potentially promising for consistently rainy regions, offering a truly unique way to make your own home electricity.
These innovations demonstrate that the quest to produce your own power is continuously evolving, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible for residential energy independence.
Making Your Choice: The Path to Energy Independence
Deciding which method (or combination of methods) is right for your home boils down to a few key factors: your location’s natural resources, your budget, and your energy needs. While the dream of “free electricity” is often tied to the zero fuel cost of renewables, remember that the upfront investment is real. However, the long-term savings, environmental benefits, and the sheer satisfaction of energy independence make these investments incredibly worthwhile. With careful planning, you can truly power your home for free in the years to come.
Start by getting a professional energy audit of your home. This will pinpoint your energy consumption patterns and identify areas for efficiency improvements, which is often the first and cheapest step toward reducing your bills. Then, armed with the knowledge of your local resources, reach out to reputable installers for quotes and detailed assessments. They can help you navigate permits, incentives, and the specific requirements for your chosen system to generate free electricity sustainably.
- Is Hydropower Renewable Or Nonrenewable Resource? Sorting Out the Facts - March 3, 2026
- Hydroelectric Power Basics How Water Is Used For Electricity - February 26, 2026
- Portable Water Generators Power Off-Grid Homes and Adventures - February 25, 2026